Recommendations of the Commission
As of 1 July 2022, the statutory minimum wage is to rise to EUR 10.45. That is the recommendation of the Minimum Wage Commission. This change will benefit millions of people in Germany. But what is the Minimum Wage Commission? What is the minimum wage at the moment? And who is entitled to it?
4 min reading time
The minimum wage is to continue to rise until 2022.
The statutory minimum wage
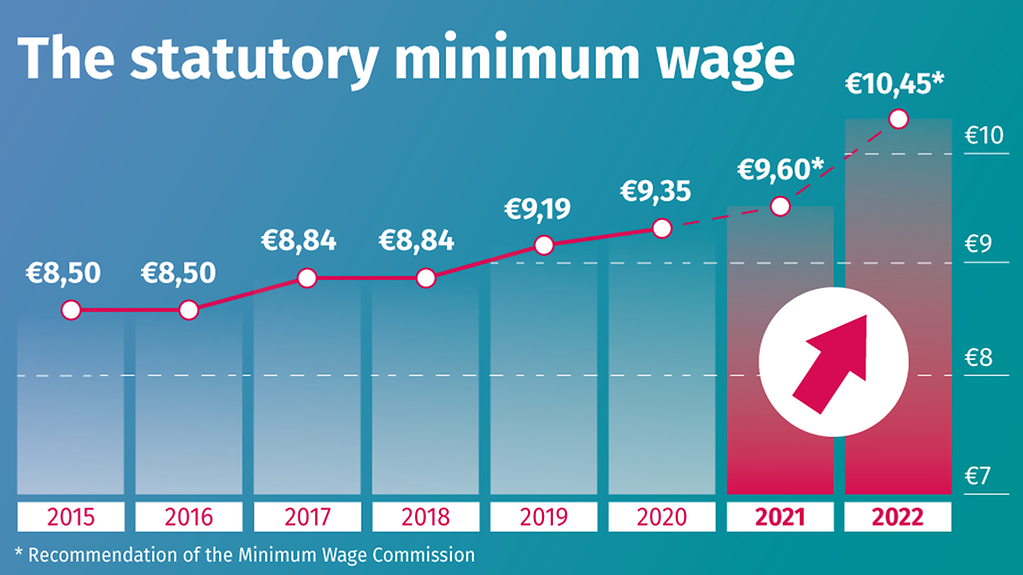
2015 €8.50
2016 €8.50
2017 €8.84
2018 €8.84
2019 €9.19
2020 €9.35
2021 €9.60*
2022 €10.45*
* Recommendation of the Minimum Wage Commission
Photo: Bundesregierung
How will the minimum wage change between now and 2022?
The Minimum Wage Commission recommends raising the minimum wage in stages, reaching EUR 10.45 as of 1 July 2022. The individual stages are listed below:
- As of 1 January 2021: EUR 9.50
- As of 1 July 2021: EUR 9.60
- As of 1 January 2022: EUR 9.82
- As of 1 July 2022: EUR 10.45
Hubertus Heil, Federal Minister of Labour and Social Affairs, will present the recommendations of the Minimum Wage Commission to the Cabinet for approval.
What is the minimum wage now and why was it introduced?
Since 1 January 2020, the gross statutory minimum wage has been EUR 9.35. The Minimum Wage Commission has recommended increasing this in several stages to EUR 10.45 as of 1 July 2022.
A general statutory minimum wage protects employees against inappropriately low pay, and thus helps ensure fair and proper competition. At the same time it ensures greater stability within the social welfare system.
The Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs’ minimum wage calculator helps establish whether or to what extent pay complies with the minimum wage, whether it is higher or lower, and what the hourly wage is.
Who is entitled to the general minimum wage?
The statutory minimum wage applies to all employees over the age of 18. Under certain conditions, interns may also be entitled to the minimum wage.
The following groups are not considered to be employees under the terms of the Minimum Wage Act:
- Trainees under the provisions of the Vocational Training Act
- Individuals performing voluntary work or undertaking voluntary service
- Participants in an employment promotion measure
- Self-employed individuals
- Long-term unemployed within the first six months of reintegration in the labour market.
Individuals who have long-term unemployment behind them are entitled to the branch-specific minimum wage immediately, however, since this is the result of collective bargaining agreements.
What about people with a mini-job?
The statutory minimum wage applies irrespective of working hours or scope of employment – so it also applies to mini-jobs. It is a gross hourly wage. The employer also pays contributions to the statutory health and old age pension insurance.
The employer must record the hours worked by people with a mini-job and must keep these records for two years, so that they can be produced should the company be audited by the customs authorities.
When are employers obliged to keep documentation?
Employers have a general obligation to document all minor employment as well as employment in the branches laid out in the Schwarzarbeitsbekämpfungsgesetz (Act to Combat Clandestine Employment). Newspaper delivery staff and employees of parcel delivery services too must keep a record of their working hours.
Is an company liable if a sub-contractor fails to comply with the provisions of the Minimum Wage Act?
A company is liable for any non-compliance with the statutory minimum wage if it sub-contracts another company to provide work or services. This liability has been part of the Arbeitnehmer-Entsendegesetz (Act on Posting of Workers) for many years. The Minimum Wage Act builds on this existing regulation, since it has proved its worth.
Who decides if the minimum wage should be changed?
An independent commission of the social partners (the employer side and the labour side), known as the Minimum Wage Commission, proposes once every two years to the German government what changes should be made to the minimum wage. It examines which level of minimum wage offers an appropriate minimum protection for employees, while allowing for fair competition and not jeopardising employment. The Commission takes its lead from changes to wages under collective bargaining agreements in Germany.
The Minimum Wage Commission also evaluates on an ongoing basis the impacts of the minimum wage, and submits its findings to the German government once every two years in the form of a report.
Who sits on the Minimum Wage Commission?
The Minimum Wage Commission consists of one chair, six voting members and two advisory members. Every five years, the leading employers’ and employees’ associations each recommend three representatives to sit on the Commission.
The two advisory members do not have voting rights and are supposed to lend their expertise to proceedings. The members are nominated by the social partners and then appointed by the German government.
Who checks that the minimum wage is actually paid? What sanctions can be imposed for non-compliance?
The customs authorities (financial control clandestine employment) are responsible.
Failure to comply with the minimum wage can result in a fine of up to EUR 500,000. Contraventions of commitments such as documentation of working hours can be penalised with a fine of up to EUR 30,000. Companies can also be excluded from public contracts.
If employees have questions about the minimum wage, who can they turn to?
The Minimum Wage Hotline is there for your complaints and for reports of any contraventions, and to answer all your questions relating to the minimum wage. The hotline is open from Monday to Thursday from 08:00 to 20:00. Just call (030) 60 28 00 28.
The customs authorities are responsible for investigating legal violations. There is also an option to go to the responsible Labour Court to demand the minimum wage.